Study finds caffeine can weaken effectiveness of certain antibiotics
Researchers discover substances bacteria can find in their natural environment trigger their alert systems
Advertisement
Ingredients of our daily diet – including caffeine – can influence the resistance of bacteria to antibiotics. This has been shown in a new study by a team of researchers at the Universities of Tübingen and Würzburg led by Professor Ana Rita Brochado. They discovered bacteria such as Escherichia coli (E. coli) orchestrate complex regulatory cascades to react to chemical stimuli from their direct environment which can influence the effectiveness of antimicrobial drugs.
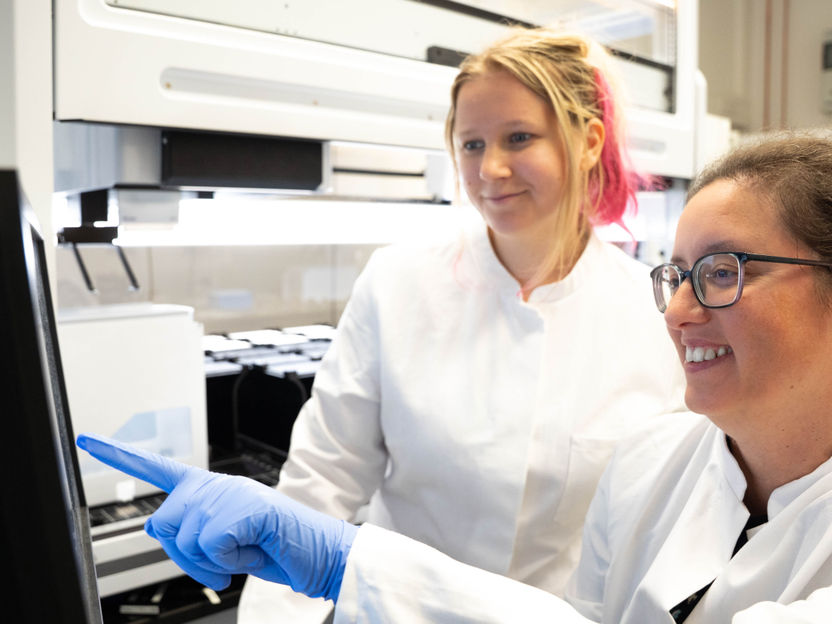

Scientist Ana Rita Brochado (r) and her lab team member Laura Sniegula look at data from the pipetting robot. With this laboratory tool the team investigated the effect of 94 different substances.
Leon Kokkoliadis, Universität Tübingen
In a systematic screening, Brochado's team investigated how 94 different substances – including antibiotics, prescription drugs, and food ingredients – influence the expression of key gene regulators and transport proteins of the bacterium E. coli, a potential pathogen. Transport proteins function as pores and pumps in the bacterial envelope and control which substances enter or leave the cell. A finely tuned balance of these mechanisms is crucial for the survival of bacteria.
Researchers describe phenomenon as an ‘antagonistic interaction’
“Our data show that several substances can subtly but systematically influence gene regulation in bacteria,” says PhD student Christoph Binsfeld, first author of the study. The findings suggest even everyday substances without a direct antimicrobial effect – e.g. caffeinated drinks – can impact certain gene regulators that control transport proteins, thereby changing what enters and leaves the bacterium. “Caffeine triggers a cascade of events starting with the gene regulator Rob and culminating in the change of several transport proteins in E. coli – which in turn leads to a reduced uptake of antibiotics such as ciprofloxacin,” explains Ana Rita Brochado. This results in caffeine weakening the effect of this antibiotic. The researchers describe this phenomenon as an ‘antagonistic interaction.’
This weakening effect of certain antibiotics was not detectable in Salmonella enterica, a pathogen closely related to E. coli. This shows that even in similar bacterial species, the same environmental stimuli can lead to different reactions – possibly due to differences in transport pathways or their contribution to antibiotic uptake. President Prof. Dr. Dr. h.c. (Dōshisha) Karla Pollmann emphasizes: “Such fundamental research into the effect of substances consumed on a daily basis underscores the vital role of science in understanding and resolving real-world problems.”
The study, which has been published in the scientific journal PLOS Biology, makes an important contribution to the understanding of what is called ‘low-level’ antibiotic resistance, which is not due to classic resistance genes, but to regulation and environmental adaptation. This could have implications for future therapeutic approaches, including what is taken during treatment and in what amount, and whether another drug or food ingredient – should be given greater consideration.